Skin Care Advice
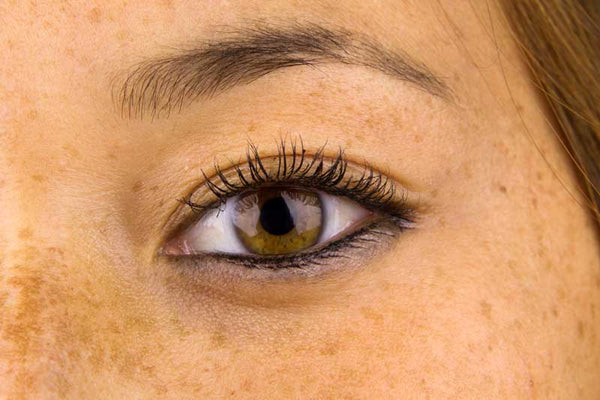
The Effects of Sun Damage and How to Prevent Them
Outdoor activities are extremely popular, especially in the summer, and it can feel awesome to get outside and soak in some vitamin D. However, many underestimate the dangers of sun damage to their skin. Sunburn isn’t the first hint that your skin is being damaged; in fact, even tanning is a visible sign of sun damaged skin. Sun damage is one of the leading causes of visible aging on the skin, manifesting in the following ways:
- Pigmentation issues – Overexposure to the sun can lead to various uneven pigmentation issues, such as sun spots/age spots, freckles, and dark blotches on the skin.
- Wrinkles – While wrinkles naturally occur through normal aging, sun damage can accelerate the formation of wrinkles, partly because UV rays can cause a loss in collagen and elastin, two of the proteins responsible for maintaining healthy skin. Without these essential structural proteins, the skin can become thinner and more easily wrinkled.
- Leathery skin – Tough, leathery skin is also caused by excess sun exposure. Just as with wrinkles, this damage is largely due to the loss of collagen and elastin in the skin, causing skin to be less full and supple.
- Skin cancers – Skin cancer is the most serious threat of sun damage on skin. Excess sun exposure can cause dark spots, which can lead to malignant melanoma, and dry scaly patches known as actinic keratosis, which can also develop into skin cancer.
These visible signs of sun damaged skin are all part of photoaging, a term that’s used to describe changes to the skin caused by sun damage. But you don’t have to get burned; here are some of the best ways to fight and prevent photoaging and maintain healthy skin:

Minimize outdoor activity between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m.

Apply sunscreen regularly

Wear protective clothing


Note: When using retinol, it’s best to apply it at night since retinol can break down in the sun.